FIELD GUIDE
- All
- Art
- Anthropology
- Biology
- Cognition
- Complexity
- Computation
- Culture
- Education
- Linguistics
- Mathematics
- Music
- Philosophy
- Physics
AESTHETICSThe study and systematic exploration of beauty and taste across individuals and cultures, sometimes also synonymous with the philosophy of art.
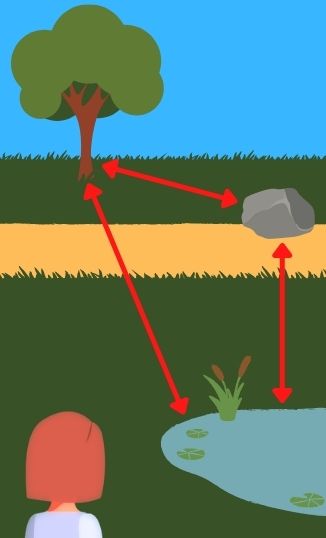
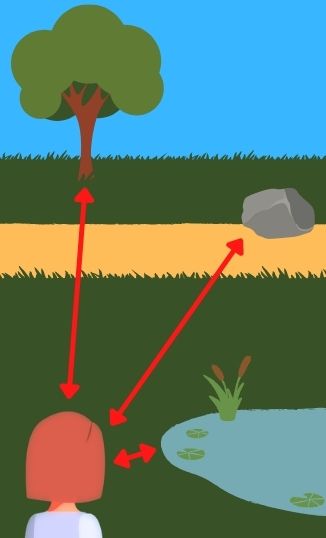
ALLOCENTRIC REPRESENTATIONSpatial representation where one denotes the location of something else in reference to another object, independent of oneself.
ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKComputational system vaguely inspired by biological neural networks that operates a large network of relatively simple computing nodes.
BASAL COGNITIONCognitive-like capabilities exhibited in biological systems without complex nervous systems, including non-neural animals, plants, fungi, single-celled life forms or cell networks within an organism.
BIOLOGICAL NEURAL NETWORKPhysiological tissue composed by neurons and other specialized cells; linked to higher cognitive functions in some animals.
BIOPHYSICSStudy of physical phenomena in biological systems, on scales spanning molecules, cells, tissues and organisms, using the principles and methods of physics.
BLACK HOLERegion of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing (no particles or even electromagnetic radiation such as light) can escape from it.
BLACK HOLE INFO. PARADOXAlleged loss of physical states information of systems falling inside a black hole according to general relativity, which would violate unitarity, a core principle of quantum mechanics.
CAUSALITYInfluence by which one event, process, state, or object (a cause) contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an effect).
CELLMinimal observed unit of conventionally attributed full biological function. Typically, a complex assembly of microscopic molecular machinery.
CHORDIn music, any harmonic set of pitches/frequencies consisting of multiple notes that are heard as if sounding simultaneously.
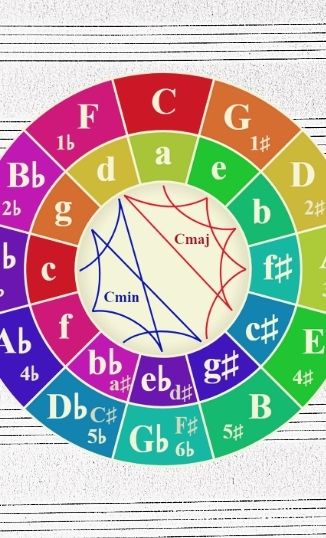
CIRCLE OF FIFTHSIn music theory, way of organizing the 12 chromatic pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths./br>
CLASSICAL PHYSICSCollection of models and theories that describe phenomena at the macroscopic and astrophysical scales; historically, the physical theories predating the discovery of quantum phenomena.
COGNITIVE ARCHAEOLOGYTheoretical perspective in archaeology that focuses on the ancient mind, trying to understand human cognitive evolution and symbolic structures from material record.
COLLECTIVE COMPUTATIONThe phenomenon of information processing by a large group of individuals in interaction, each of which processes information individually and communicates with other individuals.
COLLECTIVE INTELLIGENCEBehaviour exhibited by a system, emerging from the collaboration, collective efforts, and competition of the individuals within it.
COMMONSENSE REASONINGIn artificial intelligence, human-like ability to make presumptions about the type and essence of ordinary situations humans encounter every day.
COMMUNICATION THEORYIn information theory, communication theories examine, typically in a mathematical fashion, the technical process of information exchange.
COMPLEX SYSTEMPhysical system with a large amount of components that interact to generate intricate emergent dynamics, self-organization, or chaotic behaviour.
CONCEPTUAL SPACEGeometric structure representing quality dimensions, which denote basic features of concepts and objects, such as weight, color, taste, temperature, pitch, and the three ordinary spatial dimensions.
CONFIGURATION SPACEAbstract set of all static positions of a mechanical system, often giving a simple high-dimensional geometric description of complex low-dimensional machines.
CONTINUITYPerceived experience of qualities that vary smoothly over spatial or temporal extension. Abstracted in the real numbers. Often invoked in contrast to discreteness.
COUNTABLE SETSet with the same cardinality as some subset of the standard natural numbers. A countable set can be labelled by a (possibly infinite) sequence of natural numbers.
CRYPTOGRAPHYStudy of secure communications techniques that allow only the sender and intended recipient of a message to view its contents.
CULTURAL DATA ANALYSISMultidisciplinary science that uses computational, visualization, and big data methods for the exploration of contemporary and historical cultures.
DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY Study of the process by which living organisms grow and develop, including phenomena such as regeneration, metamorphosis and cell differentiation.
DISCRETENESS Perceived experience and abstraction of qualities that vary abruptly over spatial or temporal extension. Abstracted in countable sets. Often invoked in contrast to continuity.
EGOCENTRIC REPRESENTATIONSpatial representation where one denotes the location of something else in reference to oneself.
EMBEDDINGA general concept in geometry or data science that refers to the phenomenon of a region, shape or structure sitting inside of a larger or higher-dimensional ambient space.
EMBODIED COGNITIONTheory which posits that cognitive systems should be considered in all their extension (body), not just in the centers of information processing (brain).
EMERGENT SPACE(TIME) In physics, view that considers space(time) not as the fundamental structure of reality, but as emergent from a more fundamental, non-spatial entity or phenomenon.
EMERGENTISM Philosophical view which posits that collectives can exhibit behaviour that cannot be inferred from knowledge of the individuals.
EVOLUTION Process by which a population of individuals changes over time through mechanisms such as reproduction, inheritance, mutation and selection.
EXTENDED MIND The idea that contents of the mind appear and are articulated in the world. Examples are written languages, cities or technology.
GENERAL RELATIVITY Geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916 and current description of gravitation in modern physics.
GRID CELL Type of neuron that fires at regular intervals as an animal navigates an open area, allowing it to understand its position in space by storing and integrating information about location, distance, and direction.
INFORMATION THEORYDiscipline dedicated to the scientific study of the quantification, storage, and communication of digital information.
LINGUISTICS Discipline dedicated to the study of languages. For human populations it entails the study of phonology, morphology, syntax and semantics.
MORPHOGENESIS Biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of developmental biology along with growth and patterning.
MORPHOLOGICAL SPACE Geometric representation of the possible form, shape or structure of an organism. In a morphospace, axis and points correspond to organism characters and individual organisms, respectively.
MUSIC THEORYStudy of the practices and possibilities of music, including musical notation, scholar’s views on music from antiquity to the present, and definitions of processes and general principles in music.
NEUROPLASTICITYProcess by which biological neural networks rearrange and reorganize themselves leading to adaptation and change of learned behaviours.
NON-NEURAL BIOELECTRICITY Non-neural electrical processes in biological systems, such as bioelectrical pattern recognition, that may allow information processing and hence non-neural cognition.
ONTOGENYProcess by which an individual is formed. In pluricellular organisms, the process from the fertilization of an egg to the formation of an adult.
PHASE SPACEAbstract set of all the states of a physical system, often giving a geometric description of the kinematics of a dynamical system.
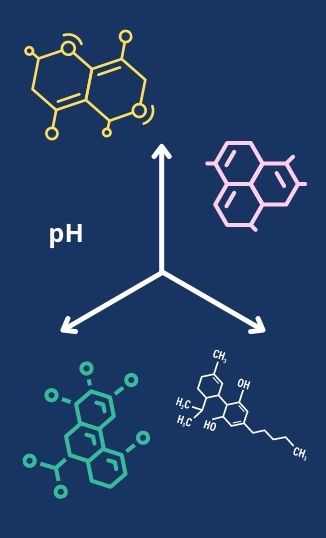
PHYSIOLOGICAL SPACEGeometric representation of the physiological variables in a biological system, such as enzyme concentration, pH, electrochemical activity, etc.
PLACE CELL Type of neuron that becomes active when an animal enters a particular place in its environment. Place cells are thought to act collectively as a cognitive representation of a specific location in space.
QUANTUM GRAVITY The sought after theory (or family of theories) that may unify general relativity and quantum mechanics to account for gravitational phenomena at the scales of fundamental particles.
QUANTUM INFORMATION In physics, information of the state of a quantum system. It is the basic entity of study in quantum information theory.
QUANTUM PHYSICS Collection of models and theories that describe phenomena at the near-atomic and subatomic levels; characteristic quantum phenomena may present state entanglement and observational indeterminacy.
REAL NUMBERS Mathematical object capturing the formal structure of geometric distances and approximating sequences; typically considered as the mathematical model of physical quantities.
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE Branch of medicine that develops methods to regrow, repair or replace damaged or diseased cells, organs or tissues to restore or establish normal function.
RELATIVITY THEORY Physical theory that provides the most accurate, compact and mathematically elegant model to date for the relation between observers of classical phenomena.
SEMANTICS Study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics and computer science.
SPACETIME SINGULARITY Extreme gravity scenarios, such as the center of black holes, where general relativity prediction makes spacetime itself ill-defined, often interpreted as a limitation of the theory.
SPATIAL COGNITIONCognition concerned with the acquisition, organization, utilization, and revision of knowledge about spatial environments.
SPATIAL REASONINGArea of artificial intelligence seeking representing and reasoning about spatial knowledge, as well as developing automatic systems for navigating and understanding space.
SYNTHETIC BIOLOGYMultidisciplinary area of research that seeks to create new biological parts, devices, and systems, or to redesign systems that are already found in nature.
THEORETICAL BIOLOGY Discipline dedicated to the formal modelling of biological systems by developing mathematical and philosophical frameworks.
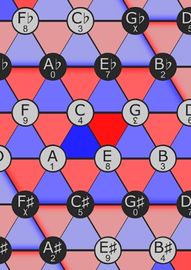
TONNETZConceptual lattice diagram representing tonal space first described by Euler, which can be used to show traditional harmonic relationships in European classical music.
TOPOLOGYIn mathematics, study of the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending.
VOICE LEADINGLinear progression of individual melodic lines and their interaction with one another to create harmonies, typically following the principles of common-practice harmony and counterpoint.
WORD CLASSSet of words that exhibit the same grammatical or syntactic properties. Examples of word classes, also called lexical categories or parts of speech, are nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions…